It is shown that changes in the absorption coefficient due to different levels of semiconductor doping. The emissivity depends on carrier concentration in the silicon samples.

Comparison Between Spectral Normal Emissivity Of Silica 162 M Thick Download Scientific Diagram
Articles journal articles other e-resources.

. This result is of great interest to the LIGO Voyager gravitational wave interferometer project since it would. A blackbody source is heated to various known. The temperature dependences of the spectral and total hemispherical emissivities of silicon have been experimentally determined by using a technique which combines isothermal electron beam heating with in situ optical measurements.
This result is of great interest to the LIGO. Emission spectra were used to deduce the absorption coefficient for phosphorus-doped silicon samples for wavelengths between 11 and 16 μm in. The surface temperature is measured in-situ and in real-time during a high-temperature process in a vacuum system by using the linear polarization property of radiation.
Emissivity is defined as the ratio of the energy radiated from a materials surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter known as a blackbody at the same temperature and wavelength and under the same viewing conditions. Emissivity is the ratio of the energy radiated from a materials surface to that radiated from a perfect emitter. SEMATECH on the temperature-dependent emissivity of silicon- For RTP pyrometers are the instruments of choice for related materials and structures are presented in this study.
The formula for the reflection and emissivity of electromagnetic radiation of a semitransparent semiconductor wafer is presented. Silicon emissivity as a function of temperature. The emissivity value follow a linear dependency in the 120-260 K temperature range.
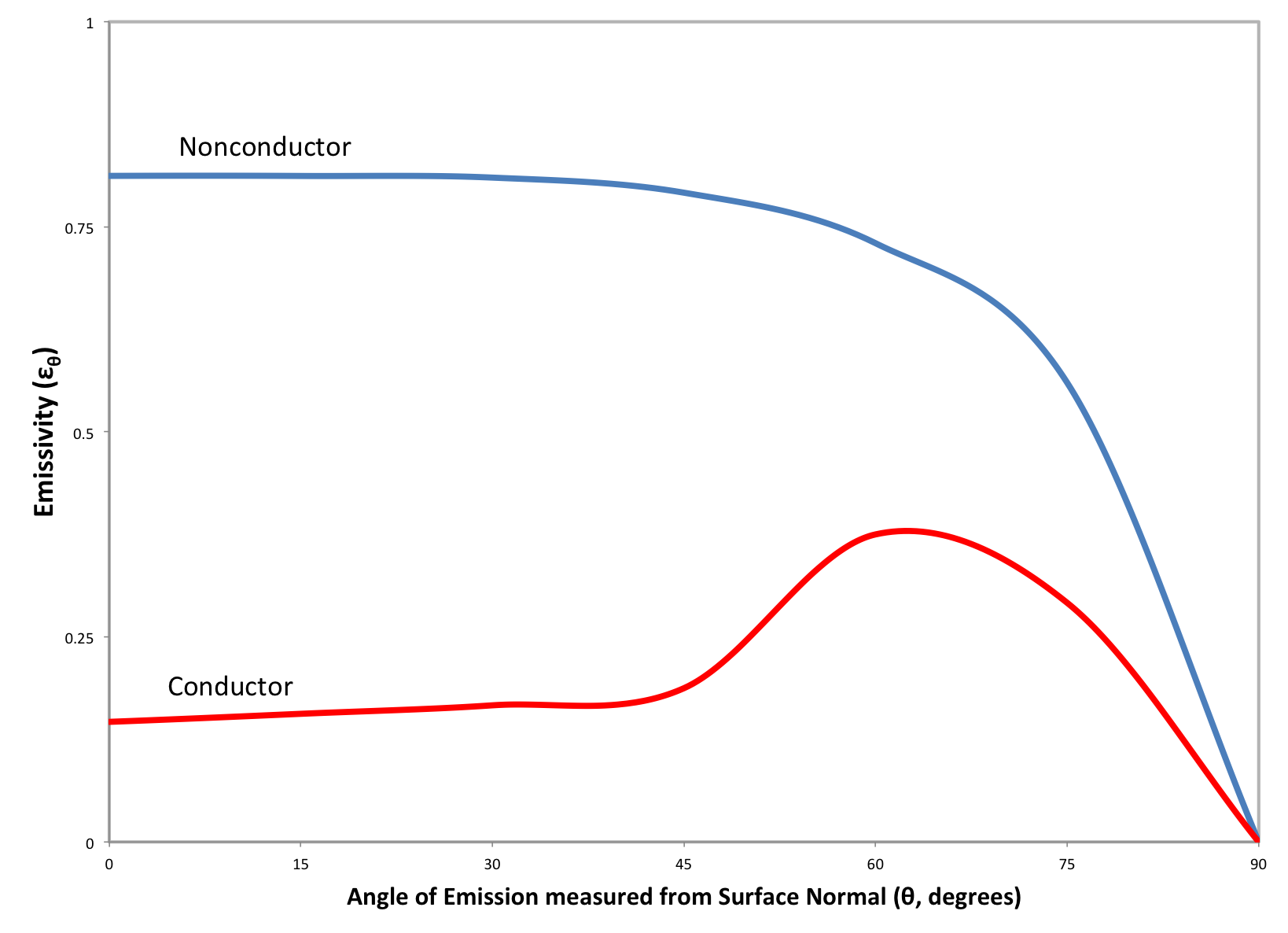
Modeling of emissivities is. These results have been acquired using a spectral emissometer. A blackbody is an example of a perfect emitter it has an emissivity of 1 while a perfect reflector or white body has an emissivity of 0.
For heavily doped specimens the total emissivity remains approximately constant at 07 between 200 and 800 C because the carrier concentration is high even at room temperature and the additional thermal generation of carriers produces an insignificant change in the total emissivity. Very hot materials emit visible light and materials at or around room temperature emit infrared light. Emissivity is the ratio of the thermal radiation of a surface relative to the radiation of an ideal black body at the same temperature ratio between 0 and 1.
Articles all catalog articles website. Select search scope currently. The emissivity of silicon was observed in the spectral region from 04 to 15 mu at various temperatures from 340K to 1070K by using two n-type.
Also the experimental curve for both runs is steeper in the beginning compared to the simulated. In order to measure the total temperature-dependent emissivity of Silicon ϵT. An emissivity of 0 means that the material is a perfect reflector whereas a ratio.
The temperature dependences of the spectral and total hemispherical emissivities of silicon have been experimentally determined by using a technique which combines isothermal electron beam heating with in situ optical measurements. A method and system for measuring remotely the surface temperature of a silicon wafer and layers without the need to know the surface emissivity. Low emissivity high-temperature tantalum thin film coatings for silicon devices Journal of Vacuum Science Technology A.
In this paper we present the temperature-dependent emissivity of a silicon sample estimated from its cool-down curve in a constant low temperature environment approx 82K. In order to answer this question first we must understand emissivity. Phonons contribute to emis- of this wafer is negligible at room temperature while at sivity changes.
The emissivity value follow a linear dependency in the 120-260 K temperature range. In this paper we present the temperature-dependent emissivity of a silicon sample estimated from its cool-down curve in a constant low temperature environment 82K. The wavelength region of 12 to 35 microns and at room temperature.
As can be seen the cooling down time of the Si sample from room temperature to 123 K was coincidentally about the same as it had a constant emissivity of 05. The silicon wafer near room temperature is semitransparent at a wavelength more than 11 spl mum which makes emissivity behaviors complicated. In this paper we present the temperature-dependent emissivity of a silicon sample estimated from its cool-down curve in a constant low temperature environment 82K.
Catalog books media. After showing a broad minimum at. This result is of great interest to the LIGO Voyager gravitational wave interferometer.
Does emissivity change with temperature. Emissivity behaviors of a silicon semiconductor wafer near room temperature have been measured and considered from the view point of spectral directional and polarized properties. The total emissivity of four samples of silicon of different resistivities is measured in the temperature range 880-1550 K.
Emission spectra were used to deduce the absorption coefficient for phosphorusdoped silicon samples for wavelengths between 11 and 16 μm in. The emissivity value follow a linear dependency in the 120260 K temperature range. As the temperature increases the emissivity increases shows a maximum at about 950 K and then starts decreasing.
Phonons contribute to emis- of this wafer is negligible at room temperature while at sivity changes. It is a dimensionless number between 0 for a perfect reflector and 1 for a perfect emitter. Vacuum Surfaces and Films 2013 John Joannopoulos.
The variation of emissivity and absorption between different parts of a production wafer results in nonuniform wafer temperature.
Total Emissivity Of Low Doped Silicon As A Function Of Temperature Download Scientific Diagram

Comparison Between Spectral Normal Emissivity Of Silica 162 M Thick Download Scientific Diagram

Temperature Dependence Of The Normal Spectral Emissivity Of The Sio 2 Download Scientific Diagram

Sato S 1 Spectral Emissivity Of N Si Of Thickness 1770 Mm And Doping Download Scientific Diagram
Total Normal Emissivities Of Selected Materials Neutrium
![]()
Emissivity Of The Bilayer Structure Under Normal Incidence Vs The Download Scientific Diagram

Room Temperature Emissivity With The Integrated Sphere Measurement Download Scientific Diagram

Results Of Simulation Of Emissivity As Function Of Wavelength For Download Scientific Diagram
0 comments
Post a Comment